Image credit: Allen Institute for Brain Science / Nature
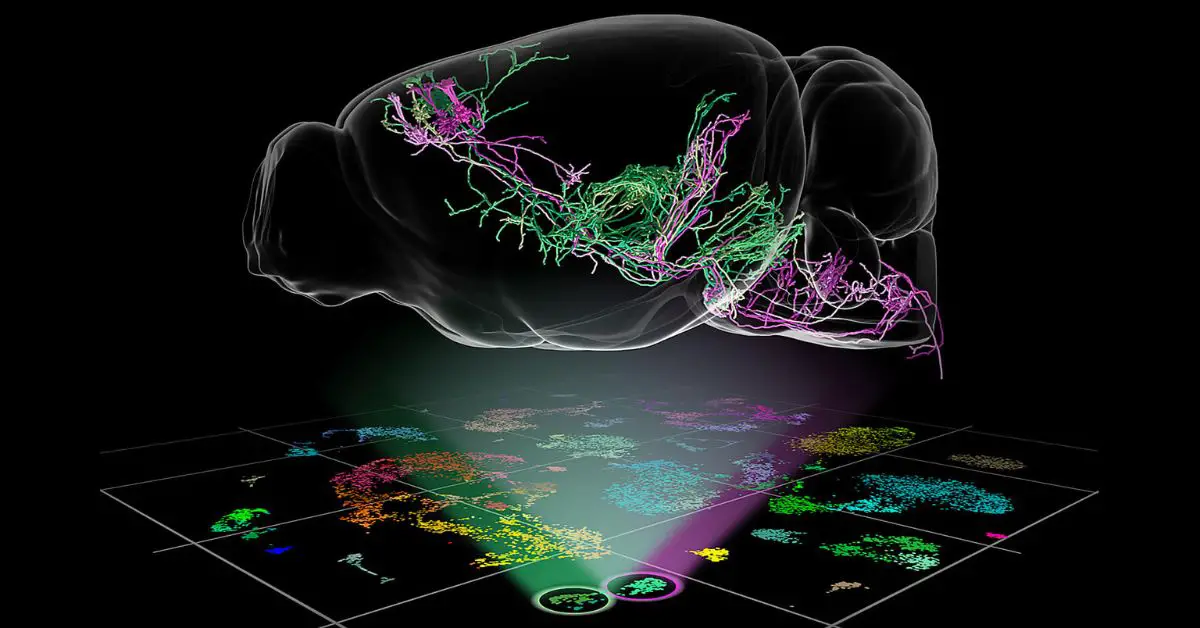
In a stunning scientific breakthrough, researchers have created the most detailed functional map of a mammalian brain to date — using just a tiny fragment of a mouse brain. The result? A dazzling 3D reconstruction of 84,000 neurons and over 500 million synapses that resembles the cosmic complexity of a galaxy. This pioneering research may offer critical insights into how the human brain works and what goes wrong in neurological diseases.
A Brain Map Like No Other
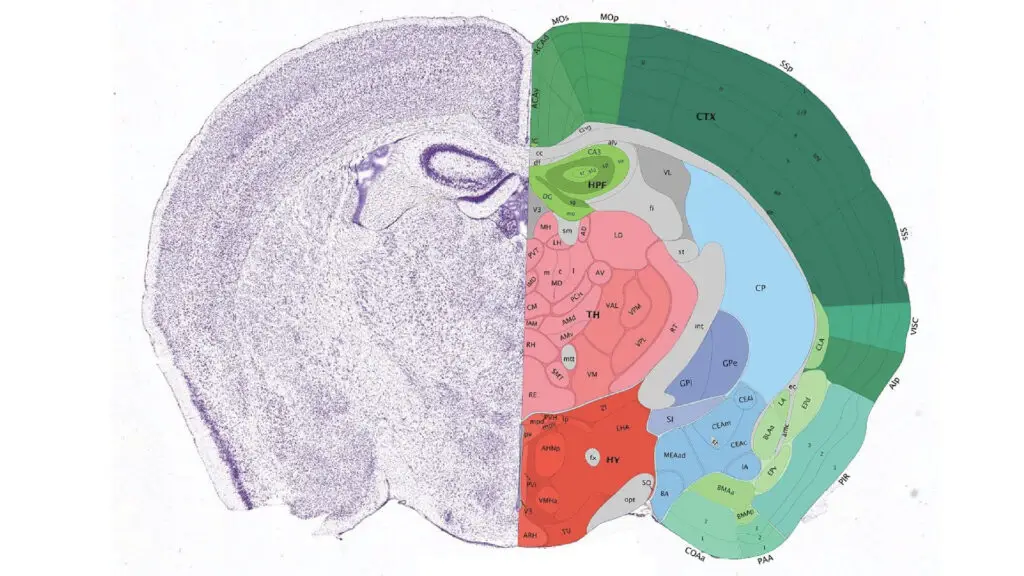
Image credit: Allen Institute for Brain Science / Nature
The mapped tissue, no larger than a poppy seed, was taken from the visual cortex of a genetically engineered mouse. Scientists used advanced electron microscopy and artificial intelligence to trace how the neurons communicate across dense, tangled networks of axons and dendrites — the thread-like extensions through which nerve signals travel.
If stretched out, the microscopic wiring captured in this study would span over 5 kilometers, a staggering feat considering it came from such a minuscule area. Forrest Collman, a senior researcher at the Allen Institute for Brain Science and one of the project’s leaders, compared the intricate design to “looking at galaxies.” It’s a poetic metaphor — and an accurate one.
How the Study Was Conducted
To begin, scientists showed the mouse a series of video clips including scenes from sci-fi movies like The Matrix, sports reels, nature footage, and animation. The mouse had been genetically modified so its neurons would glow when activated, allowing researchers to observe brain activity in real time as the animal processed the images.
Afterward, the brain tissue was sliced into over 25,000 ultra-thin sections. Using a powerful electron microscope, scientists captured nearly 100 million high-resolution images. These were stitched together into a single, ultra-detailed 3D model, forming a complete wiring diagram of a functioning piece of brain tissue.
Artificial intelligence played a crucial role in this process. Neural connections were digitally color-coded and traced, allowing researchers to follow individual signal paths across the complex neural web.
Why This Matters for Human Health
While the study was conducted on mice, the implications are enormous for humans. Understanding how neurons connect and communicate is essential to unraveling the mysteries of memory, emotion, learning, and disease. Disorders like Alzheimer’s, autism, and epilepsy may be rooted in microscopic disruptions to these neural pathways.
This mouse brain map is being compared to the Human Genome Project for its potential to revolutionize medicine. Just as sequencing the human genome opened doors to genetic therapies, mapping neural circuits may lead to targeted treatments for brain disorders.
According to Sebastian Seung, a computational neuroscientist at Princeton and another lead on the project, this research “gives us the first opportunity to detect abnormal wiring patterns that underlie disease.” Future efforts will aim to map an entire mouse brain, an endeavor expected to push technological and scientific limits even further.
A New Era for Brain Science
The research, published in Nature, is already being called a landmark achievement in connectomics — the study of neural connections. The dataset is publicly available, enabling neuroscientists worldwide to explore, expand, and build upon the findings.
Harvard researchers who reviewed the work noted that it represents “a giant leap forward” and provides an “invaluable community resource for future discovery.”
As we stand on the edge of a new frontier in neuroscience, this small but mighty piece of mouse brain may help unlock the most profound mysteries of the human mind — from consciousness to cognition, memory to emotion.
Maybe you also like:
- Scientists Have Cloned Real Dire wolves—And They’re Alive Today
- Woolly Mammoths May Roam Again by 2028
- De-Extinction: Hope or Hubris? The Ethics of Bringing Species Back to Life
Follow me on X, YouTube,
Pinterest , Facebook
Threads and Instagram
For more updates visit: flashpointnews.com.br


6 thoughts on “Mapping the Mouse Brain: A Leap Toward Understanding Human Intelligence”